Manuscript accepted on : 01-08-2025
Published online on: 10-09-2025
Plagiarism Check: Yes
Reviewed by: Dr. Shah Tapas
Second Review by: Dr. Sarraa Dhiaa Kasim
Final Approval by: Dr. Eugene A. Silow
Formulation and Evaluation of Nanoemulgel of Econazole Nitrate to Treat the Topical Fungal Infection
Harsha Hiraman Tarare , Amit Gaiwkawad*
, Amit Gaiwkawad* and Laxmikant Borse
and Laxmikant Borse
Department of pharmaceutics, Sandip Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences , Nashik, Maharashtra, India.
Corresponding Author Email:amit.gaikwad@sandippharmacy.org
ABSTRACT: Econazole nitrate, an imidazole ring-containing broad-spectrum antifungal drug, is used to treat Dermatomycosis furfuracea, Foot mycosis and Groin dermatophytosis. This work focuses on the formulation and assessment of nanoemulgels generated from Nano emulsions using high-speed homogenization. Nanoemulgel has various benefits over creams and ointments, one of which is that the drug is delivered to intended location more quickly. Mycosis for skin belong to the most common dermatological syndrome in the globe. Topical treatment improves efficacy and permeability. The characterization of the econazole was done by physical appearance , melting point , UV , IR , DSC. Solubility of Econazole in different oils and surfactants like Almond oil , Oleic acid , Olive oil, Tween 80,Tween 40, Span 80 and PEG 400 , Ethanol. According to solubility the surfactant, oil and co-surfactant was chosen. The nanoemulsion of Econazole with oleic acid, tween 80, PEG400 was made . Nanoemulsion was then characterized by entrapment efficiency, Globular size(particle size),zeta potential, drug content . After getting optimized batch the corbopol 940 use as gelling agent , was encorporated into the nanoemulsion , and nanoemulgel was formed . The nanoemulgel properties were assessed by measuring drug content, viscosity pH. Drug release from nanoemulgel was done by franze diffusion cell . The melting point of the Econazole was found to be 1630C. UV Spectroscopy of Econazole gives wavelength 218 nm for the topical formulation . FTIR gives the functional groups present in pure Econazole structure.. The solubility of Econazole is highest in oleic acid was 66 mg/ml , surfactant Tween 80 was 11.23 mg/ml, and co surfactant PEG400 was 3.8 mg/ml . The Particle size of the nanoemulsion was found to be 192.4 nm with PDI is 0.209. The zeta potential is -30.96 mV and the % drug release is 94.2% over 24 Hrs which results in sustained and controlled drug release from the formulation. And follows higuchi order kinetics. The DSC of pure drug and final formulation of nanoemulgel was obtained which explains that decrease in melting point from pure drug(167.950C) to nanoemulgel ( 104.230 C)that the crystallinity decreases and goes toward amorphous which increase solubility. Potential Amorphization or interaction of Econazole with nanoemulgel matrix. Drug content was 96.08% and spreadability was 29.41 gm.cm/sec, and gel was easily spreads through skin. Antifungal study gives the larger zone of inhibition of the optimized formulation batch of nanoemulgel compared to the marketed formulation. Stability study was done at different temperature conditions and changes in pH, viscosity, drug content, gelling capacity was noted.
KEYWORDS: Econazole nitrate; High speed homogenization; Nanoemulgel; Nanoemulsion; Solubility
| Copy the following to cite this article: Tarare H. H, Gaiwkawad A, Borse L. Formulation and Evaluation of Nanoemulgel of Econazole Nitrate to Treat the Topical Fungal Infection. Biotech Res Asia 2025;22(3). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Tarare H. H, Gaiwkawad A, Borse L. Formulation and Evaluation of Nanoemulgel of Econazole Nitrate to Treat the Topical Fungal Infection. Biotech Res Asia 2025;22(3). Available from: https://bit.ly/3K8Mji7 |
Introduction
Cutaneous ringworm, Foot mycosis and Intertriginous candidiasis are typical surface mycosis diseases. Cutaneous ringworm and Foot mycosis are keratinophilic fungi illnesses that spread via household livestock also with surrounding respectively. Uncontrolled perspiration and impaired blood flow are the primary risk factors for , Foot mycosis , Intertriginous candidiasis can arise in people who have diseases that affect host defense mechanisms, such as pregnancy, cancer, high blood sugar condition, or steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.1 Skin illnesses in humans are prevalent and can lead to consequences if not correctly prevented. A different antifungal drugs are used to cure the mycosis skin infections, however major disease-causing fungi, especially yeasts, can acquire non-susceptibility to antifungal drugs. The consequences of localized and internal antifungal drug might occasionally limit their usage. Nanoparticles reduce the likelihood of systemic adverse effects while treating skin infections.2 Because of the negative consequences of long-term administration of antifungal medicines used to treat dermatophytic diseases such as tinea unguium, there is an urgent need for innovative antifungal treatments with increased absorption and low side effects. Nano formulations represent a viable option in this area. Topical formulations can penetrate the skin’s higher layers, such as the stratum corneum, releasing therapeutic amounts of medicines.3 Econazole nitrate, an imidazole compound, shows antifungal action opposed a wide variety of mycosis organisms. Typically, it treats yeast infections caused by common candida species.
Econazole nitrate inhibits the enzyme microsomal monooxygenase, preventing the body from producing ergosterol. This increases cell permeability, allowing contents to seep out and leading to cell death. Approximately 97% of the drug binds to serum albumin and globulins, with low being penetrates when administered cutaneously .4 Most market formulations use a greater dose drug to attain optimal therapeutic outcomes. Furthermore, the drug is slowly incorporated, resulting in drug buildup beneath the keratinized layer that slows its transit across skin. Thus, regulating active ingredient liberation will increase the effectiveness of Econazole nanoemulgel.5 Cutaneous novel drug delivery system ,nanoemulgel have been proven to enhance the systemic penetration , pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and overall medicated efficacy of hydrobhobic drugs. In current period , their usage has risen due to better patient adherence. This is widely used due to the benefits of nanoemulgels, due to their noninvasive nature, ability to bypass alimentary and digestive tract toxicity, better medicated and risk assessment , and ease of application.6
An exceptional drug delivery system should provide optimum therapeutic benefit while minimizing toxicity. Nano-sized drug delivery systems, such as nanoemulsions (NE) with 50-200 nm sized droplets maintained by surface-active agents, are regarded a viable alternative to traditional methods. Nanoemulsion formed as water-in-oil (W/O), oil-in-water (O/W), or multiple emulsions (W/O/W) systems, which have different strengths related to traditional colloidal mixtures. Benefits include: (1) Precise drug transport to affected tissues due to the increased interface provided by their ultrafine droplet distribution; (2) The ability to protect drugs from water induced cleavage and enzyme mediated degradation (3) Improved therapeutic compound loading, aqueous compatibility, and bioefficacy (4) Reduced personalized response variations and (5) The ability to achieve gradual drug administration. Because of these benefits, NE is an excellent platform for drug delivery systems.7
Material and Method
Materials
Econazole nitrate purches from Mahrshee Labortaries Pvt. Lit , Panoli, Ankleshwar. Tween 80, PEG400, Oleic acid, Triethanolamine, carbopol 940 used from Research-lab fine chem industries, Mumbai which was available in college. All the ingredients and solvents use are with analytical grade.
Characterization of Econazole Nitrate
Melting point
The melting point of the Econazole was measured by open capillary method. The Econazole was administered through a glass capillary with a flame sealed opening. The capillary was then placed into the melting point device and melting point was recorded.
Preparation of stock solution
10mg of Econazole was dissolved into 10 ml of water forms 1000 ppm solution, from this 0.2 ml pippet out and dissolve in 10ml methanol as solvent to form 20ppm solution and the absorbance spectra was taken. Now for calibration curve take 1ml from 1000ppm solution and dilute to 10ml methanol to form 100ppm solution, from this 100ppm take 0.5ml,1ml,1.5ml,2ml,2.5ml solution and dilute in 10 ml methanol to produce 5ppm,10ppm,15ppm,20ppm,25ppm. And absorbance was taken by UV spectroscopy.8
Fourier transfer infrared spectroscopy
FTIR spectroscopy gives crucial elucidation of morphology and chemical moieties identified in the drug-excipient interface. The IR spectra of the active API, physical mixture, were acquired with a Perkin Elmer. Rang was picked from 600-4000 cm by placing 1-2 mg of material on a holder and scanning the functional group picks. The drug-excipient interaction was also investigated using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Physical incompatibilities between the drug (Econazole) and excipients such as oil phase (oleic acid), surfactant (Tween 80), and co-surfactant (PEG 400) .9
DSC (Differential scanning calorimetry) Analysis
Thermal analysis can anticipate physicochemical interactions in formulations, allowing for the selection of chemically compatible components. DSC interaction can reveal changes in melting point and transition appearance. Peak shape, peak size, and transition temperature all change as the two components are mixed. These alterations are not related to any unfavorable interactions. DSC testing is advantageous over older procedures like TLC because it eliminates the need for long-term storage and thermal stressors to expedite the interaction. DSC investigations were conducted using DSC-60 equipment and thermal analysis data systems. Weighed drug samples of around 10 mg were placed in aluminum pans and lids were crimped with a crimping tool. Referencing was done with unfilled pan closed in the same way as the sample. Analyzed the drug, physical combination, and nano emulsion based gel at 30-3000°C at 200°C/min in nitrogen atmosphere. The device was standardized with an indium analytical standard. The DSC investigation was conducted on the drug, physical mixture, and major formulation.10
Preformulation study (for Solubility for formulation of nanoemulsion)
The solubility of Econazole was tested in a variety of solvents, including oils, surfactants, and co-surfactants.The saturated solution was made at room temperature and shaken in an orbital shaker for 48 hours. It was then examined using UV-visible spectroscopy. To create a saturated solution, excess drug was added to 2 ml solvent-containing test tubes at room temperature. The solution was then placed in an orbital shaker with an incubator (Neolab, selec) for 48 hours at 37°C. The speed should remain at 50 rpm. After 48 hours, the solution is purified by means of Whatman filter paper (0.48 μ). The collected supernatant fraction was examined with UV spectroscopy at a wavelength of 218 nm. The resulting absorbance was used in subsequent computations. Based on solubility information selection of oil phase, surfactant, co-surfactant carried out to get the better results .11 Screening oils, surfactants, and co-surfactants for nanoemulsions. The solubility of Econazole in several oils (oleic acid, almond oil, olive oil), surfactants (Tween-20, Tween 80), and cosurfactants (PEG 400, propylene glycol, transcutol-P) was tested to establish the optimal combination.12
Formulation and Optimization of Econazole Nanoemulsion
Optimization of Nanoemulsion
optimization helps to prevent fracturing or stratification in a nanoemulsion. The settings for nanoemulsion preparation were calibrated by means of a three-level Box-Behnken experimental design (BBD). The concentration of oil ( oleic acid), surfactant (PEG 400), and co-surfactant (Tween 80) were deemed independent factors, whereas globule size and entrapment efficiency were regarded as dependent variables. It made eight runs with 23 full factorial design, varying amounts of oil (2.5-3.5 mL), surfactant (0.1-0.5 mL), and co-surfactant (0.4-2 mL) was taken and 8 batchs was given with different concentration of independent variables. Nanoemulsion characterization factors, such as globule size and drug entrapment efficiency, were evaluated, and the optimal parameters were chosen based on the results.13
The Design –Expert Program 13.0.1 software was used . Significance of each factors and interactions was determined by ANOVA (analysis of variance. 7 batches are formed . The batches formed are as table 1. Below .14
Table 1 : Formulation of nanoemulsion
| Formulation code | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | Optimize batch |
| Ingredients |
|
||||||||
| Econazole (gm) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Oleic acid (ml) | 2.5 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 2.5 |
| Tween 80(ml) | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| PEG 400(ml) | 2 | 0.4 | 2 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 2 | 0.4 | 2 |
0.4 |
| Methyl paraben(ml) | 0.006 | 0.0060 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 |
| Water(ml) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
Method of preparation of Nano emulsion
Nano emulsions were created by combining oleic acid as the oil phase and distilled water as the continuous aqueous phase. Econazole 20 mg was dissolved in the oil phase using constant vertexing at room temperature. Tween 80 and PEG400 were added after the drug had been fully dissolved in oil. Under continuous vertexing, the needed amount of water was introduced to the oily solution drop by drop. The formulated Nano emulsion underwent high-speed homogenization.15
Characterization of developed Nano emulsion
Drug entrapment efficiency
The ultracentrifugation method was used to determine EE (entrapment efficiency).
Fill centrifuge tubes with 2 mL of Econazole loaded Nano emulsion . Ultracentrifuge at 30,000 rpm for 1 hours (Micro centrifuge, RM-12C). To eliminate any unentrapped drugs, the cleaned supernatant liquid was filtered using a 0.45 µm syringe filter. The sample was mixed with methanol and analyzed by UV. The EE (entrapment efficiency) was calculated using the following equation.16
% Entrapment efficiency = [ Total amount of drug added – Amount of drug in supernatant / Total amount of drug added ] × 100
Determination of particle size
ZS XPLORER used for obtaining the particle size. This particle size analyzer offers multiple possibilities. Determine the average diameter and calculate. To prevent multiscattering, Nano emulsion solutions were blended with sterile double-distilled water to the desired particle amount before testing. To reduce particulate aggregation caused by interparticle contact, a Nano emulsion was introduced to the dispersion apparatus and homogenized The analysis was repeated three times, and the mean particle dimension calculated as the z-average size + SD.17
Determination of zeta potential
The potential of Zeta in all formulations The ZEN 1002 was used to measure Nano emulsions. The electrical charge on medicated droplets was quantified. A prepared dilution of every blend was placed in an electrophoresis chamber, recorded at 25°C, and average values were calculated. Distilled water served as the dispersion medium, possessing a viscosity of 0.887 cP and a dielectric constant of 78.5 .18
Methods of preparation of nanoemulgel by encorporation of Nano emulsion
To prepare nanoemulgel from the optimally formulated Nano emulsion, as predicted by the experimental design software .0.3 grams of Carbopol 940 used as an gelling agent, following the primary screening assessments and by forming nanoemulgel by different concentrations of carbopol to produce an appropriate blend for cutaneous delivery and were carefully weighed, sieved, and stirred continuously with a magnetic stirrer by adding sufficient amount of water in the optimized batch of Nano emulsion . To create a Nano emulsion gel, add enough triethanolamine for pH adjustment , to the carbopol solution and stir thoroughly. Filling the container: The formulation was put into clean, dry containers.19
Table 2: Nanoemulgel formulation
| Ingredients | Nanoemulgel formulation |
| Nanoemulsion | 10ml containing 20mg Econazole |
| Carbopol 940 | 0.3 gm |
| Water | q. s to 50 ml |
| Triethanolamine | 0.4 ml |
Characterization of developed nanoemulgel
Drug content
A UV spectroscopic technique was used to assess the quantity of Econazole in nano-emulsions. The drug content was calculated as a proportion of the total quantity administered to the system. About 1 ml of Nano sized emulsion was diluted in methanol. and examined at 218 nm using a UV-visible Spectrophotometer.20
Viscosity
The viscosity of various nanoemulgels was measured using a Brookfield Digital Viscometer at 25°C. The viscosity of the s 43 spindle was measured at rotational rates of 10, 20, 50, and 100 rpm .21
pH
The stability and solubility of the drug are greatly impacted by pH . After combining all the ingredients, the pH of the produced nanoemulsion was assessed using a digital pH meter to make sure the formulation stays stable at physiological pH and doesn’t irritate when administerd..22
Spredability
Gel spreadability was tested using glass slides and a wooden block with a pulley on one end. Textured glass slide was installed on the compartment. Extra amount of formulation (approximately 1 gm) from several formulations was applied to the textured glass slide . Optimized formulation then pushed in between identically shaped slides. Extra gel was scraped cut away from the sides pulling the upper plate by 20 gms reduced the time it took to separate the two slides and improved spreadability. Spreadability was estimated using the formula below:
S = M × L/T
where ,
S -Spreadability
M- Weight applied to upper slide
L- Length of glass slide
T- Time taken to separate the slides completely from each other.23
Antifungal test
The antimicrobial diffusion method was implemented to investigate antifungal efficacy against candida albicans. A normal fungal culture was inoculated on Muller-Hinton agar plate. Two diffusion wells (A and B) of 6 mm width were bored into the agar. Well A contained a marketed formulation of Econazole cream, while B was filled with the developed Econazole nanoemulgel. For 48 hours the plates was incubated at 37°C. The diameter of the inhibition zone was assessed to assess antifungal activity.24
Skin penetration study using the Franz cell diffusion test
A cellular permeability assay was conducted to assess the Econazole nanoemulgel’s capacity to incorporate cutaneously and enter the bloodstream. This is necessary to establish if the drug is acceptable for epidermal application.. For diffusion membrane the egg was taken into the 0.1 M HCL solution for 30 mit CO2 bubbles comes upward then after cooling gently wash it and remaining inner yolk was removed by syringe . And the membrane for drug release study was made. The Franz cell diffusion test used PBS with a pH of 7.4.While performing the diffusion cell was heated with recirculated water and oscillating magnetic stirring to maintain a temperature of 37 ± 1°C. Samples (1 ml) were collected from the receptor compartment at predetermined intervals (2, 4, 6, and 24 hours) and poured with new phosphate buffer solution. Econazole absorbance was measured using UV spectrophotometry at 218nm. The release profile was calculated by graphing the cumulative amount of Econazole released (mg/ml of acceptor media) over time (h).25
Stability study
A stability analysis under accelerated settings was carried out in accordance with ICH guidelines to assess the physical stability of the proposed nanoemulgel formulation. For three month, the formulation was held at temperature and raised. Key characteristics such as clarity, pH, drug concentration , viscosity, and were carefully evaluated after 3 months.26
Results
Optimization of pure drug
Melting point : The melting point of the pure drug was found to be 1630C . Which fallows in between 160 -165 0C
Wavelength
The pure Econazole drug shows maximum absorbance at 218 nm wavelength. Further absorbance was taken for calibration curve .
FTIR of pure drug Econazole
 |
Figure 1: FTIR of Pure Econazole |
Aromatic C-C Streching, C-H bending are 1561.54, 826.26 respectively. Alkyl chain(Aliphatic), .Aromatic amines, Halo Compound, Imidazole, are 3109.21, 1328.90,826.26, 1132. This indicates that the drug is pure, by presence of the functional groups.
DSC
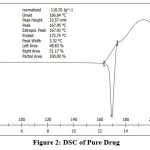 |
Figure 2: DSC of Pure Drug |
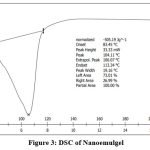 |
Figure 3: DSC of Nanoemulgel |
The DSC of the drug and the nanoemulgel gives thermal stability of formulation. Melting point of the drug is 167.950C, where as nanoemulgel has 104.11 0C.This decrease in melting point gives that the crystallinity of the formulation has been decreases as compared to pure drug, which increases the solubility of drug.
Solubility
Table 3: Solubility of Econazole
| Sr. No. | Oil , surfactants | Solubility (mg/ml) |
| 1. | Almond oil | 57 |
| 2. | Oleic acid | 66 |
| 3. | Olive oil | 6.85 |
| 4. | Tween 80 | 11.23 |
| 5. | Tween 40 | 3.87 |
| 6. | Spaan 80 | 1.2 |
| 7. | PEG 400 | 3.8 |
| 8. | Ethanol | 1.79 |
This study gives the screening of oil, surfactant , co surfactants which was use for the formulation of the nanoemulgel. Solubility of the drug was studied. Higher solubility excipients was used.
Characterization of Nanoemulsion
Entrapment Efficiency
The encapsulation efficiency expressed as percentage of drug get entrapped and calculated through the following relationship. It indicates how many amount of drug was encapsulated into the nanoemulsion. High the drug encapsulated was selected as better formulation.
Entrapment efficiency = [ Total amount of drug added – Amount of drug in supernatant / Total amount of drug added ] × 100
F7 batch shows more entrapment efficiency 82.60 %. This means the drug present in the F7 batch is more than other.
Table 4: Entrapment efficiency of Nanoemulsion
| Batch | % Entrapment Efficiency |
| F1 | 73.70 |
| F2 | 61.06 |
| F3 | 58.94 |
| F4 | 75.07 |
| F5 | 70.06 |
| F6 | 67.71 |
| F7 | 82.60 |
| F8 | 68.39 |
Particle Size
Particle size of the nanoemulsion of batch F7 is in Fig 5 , is 192.04 nm , with PDI 0.209 which gives the narrow size of the particles. It ranges from 50 – 200 nm.
 |
Figure 4: Particle size of optimized batch of nanoemulsion |
Zete potential
The zeta potential of the nanoemulsion batch F7 is -30.96 mV this shows that the nanoemulsion is moderately stable and the negative surface charge and having the conductivity of 0.201 mS/cm.
 |
Figure 5: Zeta potential optimized batch of nanoemulsion |
Characterization of Nanoemulgel
Table 5: Characterization of nanoemulgel
| Optimized Batch | Drug content (%) | pH | Spreadability (22) |
| F7 | 96.08 | 6.34 | 29.41 |
The drug content of the nanoemulgel of Econazole is 96.08 %, means the concentration of the ingredients are proper in this batch. pH is 6.34 which is suitable for the skin , Spredability is 29.41 gm.cm/sec, which shows the proper spread and application of gel.
Viscosity of Nanoemulgel
Table 6: Viscosity of nanoemulgel
| Speed rpm | Viscosity of Optimized nanoemulsion based gel | Torque(%) |
| 10 | 11360 | 94 |
| 12 | 7019 | 70 |
| 20 | 5165 | 86 |
| 30 | 2318 | 56 |
| 50 | 2265 | 55 |
Discussion: Viscosity of Nanoemulgel were determine by Brookfield DV-E viscometer. By using spindle no. 62 at 20°C Temperature viscosity was measured at 10, 20, 30, 50 rpm after 1 min. at each speed respective readings were noted in Table.
Antifungal test
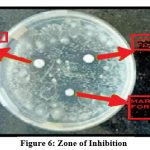 |
Figure 6: Zone of inhibition |
Table 7: Zone of inhibition
| Optimized Batch | Marketed cream | Placebo | |
| Zone of inhibition | 15mm | 12mm | 10mm |
The optimized formulation gives better zone of inhibition than marketed cream.
Drug Release
The drug release from franze cell diffusion was found to be 94.2 % for nanoemulgel and 92.458 for nanoemulsion. 99.3 % of drug was release at 10 hr of pure drug. The graph gives the drug release over 24 hr. The f7 Batch of nanoemulgel shows maximum drug release. And it displays the sustained release drug. The marketed formulation initially releases maximum drug on the other hand nanoemulgel shows controlled and sustained release drug and follows higuchi order reaction.
Table 8: Drug release from nanoemulsion , nanoemulgel and pure drug
| Time(hr) | Nanoemulsion | Nanoemulgel | Pure drug |
| 2 | 6.321 | 7.981 | 21.7 |
| 4 | 19.325 | 21.239 | 46.3 |
| 6 | 28.236 | 30.664 | 61.3 |
| 8 | 35.789 | 37.005 | 83.7 |
| 10 | 42.125 | 43.225 | 99.3 |
| 12 | 46.987 | 47.348 | |
| 14 | 56.214 | 59.505 | |
| 16 | 65.369 | 69.625 | |
| 18 | 73.896 | 75.506 | |
| 20 | 82.125 | 84.126 | |
| 22 | 87.614 | 89.991 | |
| 24 | 92.458 | 94.2 |
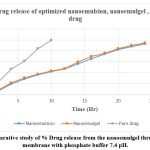 |
Figure 7: Comparative study of % Drug release from the nanoemulgel through the egg cell membrane with phosphate buffer 7.4 pH. |
Stability Study
Table 9: Stability study of the nanoemulgel, changes in pH, viscosity and drug content.
| Storage Condition (%) | pH | Appearance | Gelling capacity | Viscosity (cP) | Drug Content |
| Initial | 6.34±0.2 | Clear | +++ | 2265±6.5 | 96.08±1.9 |
| Room Temp. (25±2◦C) | |||||
| 8 days | 5.9±0.1 | Clear | +++ | 2123±10.5 | 94.2±1.3 |
| 16 days | 5.2±0.2 | Clear | +++ | 2048±14.3 | 95.2±2.1 |
| 30 days | 6.01±0.3 | Clear | +++ | 2250±16.5 | 93.2±1.9 |
| Incubator (37±2 °C) | |||||
| 8 days | 6.01±0.1 | Clear | +++ | 2200±11.3 | 94.2±1.4 |
| 16 days | 5.9±0.3 | Clear | +++ | 2145±13.5 | 95.9±1.6 |
| 30 days | 6.2±0.4 | Clear | +++ | 2198±20.5 | 96.3±0.3 |
| Refrigerated temperature (4±1 °C) | |||||
| 8 days | 5.8±0.1 | Clear | +++ | 2199±15.6 | 95.6±2.2 |
| 16 days | 5.9±0.2 | Clear | +++ | 2299±9.4 | 96.02±1.3 |
| 30 days | 6.12±0.1 | Clear | +++ | 2213±13.2 | 94.00±1.5 |
Discussion
For the treatment of fungal infection Econazole nitrate is more effective and by increasing the solubility by high speed homogenization the drug increase bioavailability and therapeutic effect. High speed homogenization is the nanonization technique which is used to reduce the particle size by applying intense shear and turbulence to break down larger droplets into smaller onces of the drug, as the spindle of the homogenizer rotates at high speed. The nanoemulsion batches formed through which the optimized batch was obtained by high entrapment efficiency and low particle size. This happened due to the surfactant and co surfactant use are in different concentrations in all formulation batches which reduce the particle size and oil use which increase solubility of drug because drug is soluble in the oil (oleic acid), This gives the sustained drug release from drug matrix, compared to the pure drug Econazole and marketed formulations. For patient compliance and maintaining the stability of formulation the nanoemulsion is converted into nanoemulgel. Carbopol 940 used as gelling agent and is compatible with drug. This gel is sustained for longer time and contact with the body surface and skin, giving more absorption through the epithelial membrane. According to the drug release study the formulation reduced dosing frequency giving more therapeutic effect as compared to the traditional drug delivery system.27
Conclusion
The research was describes the novel drug delivery system, effective treatment for drug release from skin, of the econazole for fungal cell growth inhibition, Nanoemulgel reduces first pass metabolism and increases the bioavailability the solubility of drug by nanonization technique and reducing the particle size by high speed homogenization method which gives higher stability as compared to the conventional mixing. Conventional mixing has low shear, low energy input, low stability due to larger droplets prone to creaming and phase separation. High speed homogenization is used for nanoemulsion and conventional mixing is used for coarse emulsion and pre-emulsion. In this method the nanoemulsion is under the high speed pressure that reduces the Econazole particle size by its spindle.28 Formulation of the nanoemulgel from nanoemulsion gives better stability and prevents the drug to undergo degradation, and therapeutic effectiveness which also improves the patient compliance, and reduced frequent dosing. This manages the fungal infection of foot. It gives sustained and controlled drug release from the nanoemulgel. The drug release from nanoemulgel is 94.2% over the 24 Hrs. Which follows the Higuchi order kinetics, by maintaining the therapeutic effect. Also the particle size is decrease which increase permeability and solubility.29
Acknowledgement
The authors are thank full to Mahrshee Labortaries Pvt. Lit, Panoli, Ankleshwar for providing the drug Econazole. Also thankfull to Sandip Institute of Pharmaceiutical Sciences, for provoiding the excipients requird for research.
Funding Sources
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of Interest
The authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Data Availability Statement
This statement does not apply to this article.
Ethics Statement
This research did not involve human participants, animal subjects, or any material that requires ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
This study did not involve human participants, and therefore, informed consent was not required.
Clinical Trial Registration
This research does not involve any clinical trials.
Permission to reproduce material from other sources
Not Applicable
Authors Contribution
Harsha Hiraman Tarare: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data Collection, Analysis, Funding Acquisition. Writing – Original Draft , Review and Editing.
Amit Gaikwad: Visualization, Supervision, Project Administrator.
Laxmikant Borse: Resources, Supervision, Administrative support.
References
- Davis JD. Superficial fungal infections of the skin: Tinea corporis, tinea pedis, and candida intertrigo. Primary Care Update for OB/GYNS. 1995;2(5):157-61.https://doi.org/10.1016/1068-607X(95)00033-3.
CrossRef - Rai M, Ingle A.P, Pandit R, et al.Nanotechnology for the treatment of fungal infections on human skin. The Microbiology of Skin, Soft Tissue, Bone and Joint Infections. 2017;2:169-184. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811079-9.00019-7.
CrossRef - Mousavi SA, Mokhtari A, Barani M, et al. . Advances of liposomal mediated nanocarriers for the treatment of dermatophyte infections. Heliyon. 2023;9(8):18960 . DOI : 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18960
CrossRef - Ahmad S, Patil K, Koli G, et al. Design, Development and Characterization of Econazole loaded Nanoparticles for Topical Application. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance. 2023;14(02):358-362.DOI 10.25258/ijpqa.14.2.20
CrossRef - Srivastava S, Mahor A, Singh G,et al. Formulation development, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of topical hydrogel formulation of econazole nitrate-loaded β-cyclodextrin nanosponges. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences. 2021;110(11):3702-14. DOI: 10.1016/j.xphs.2021.07.008.
CrossRef - Sharma S, Kumar A, Sahni JK, Ali J, Baboota S. Nanoemulsion based hydrogel containing omega 3 fatty acids as a surrogate of betamethasone dipropionate for topical delivery. Advanced Science Letters. 2012;6(1):221-31.DOI: https://doi.org/10.1166/asl.2012.2097.
CrossRef - Alghaith AF, Alshehri S, Alhakamy NA, Hosny KM. Development, optimization and characterization of nanoemulsion loaded with clove oil-naftifine antifungal for the management of tinea. Drug Delivery. 2021;28(1):343-56. DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1879314
CrossRef - Mandadapu G, Kolli P, Gopaiah KV, Teja R. Formulation and Evaluation of Econazole nitrate Nano emulsion for Fungal Topical Use. International Research Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences. 2024;7(6):3-8.DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.6334209.
- Kamaruzzaman AN, Jalil MT, Nor NH, Yahya MF. FTIR spectra reveal the inhibitory effects of Econazole nitrate cream on Candida Albicans biofilm. . AIP conference proceedings. 2023;2720(1).https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0137772.
CrossRef - Lin SY, Wang SL. Advances in simultaneous DSC–FTIR microspectroscopy for rapid solid-state chemical stability studies: some dipeptide drugs as examples. Advanced drug delivery reviews. 2012;64(5):461-78.DOI : 10.1016/j.addr.2012.01.009
CrossRef - Chen G, Chen J, Cheng C, Cong Y, Du C, Zhao H. Solubility and preferential solvation of econazole nitrate in binary solvent mixtures of methanol, ethanol and 1, 4-dioxane in water. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics. 2017;111:228-37.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jct.2017.03.038.
CrossRef - Priyadarshini P, Karwa P, Syed A, Asha AN. Formulation and Evaluation of Nanoemulgels for the Topical Drug Delivery of Posaconazole. Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics. 2023;13(1):33-43. DOI : https://doi.org/10.22270/jddt.v13i1.5896.
CrossRef - Chitkara A, Mangla B, Kumar P, Javed S, Ahsan W, Popli H. Design-of-experiments (DoE)-assisted fabrication of quercetin-loaded nanoemulgel and its evaluation against human skin cancer cell lines. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(11):2517. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112517
CrossRef - Nunse D, Shevalkar GB, Borse L. Innovative polymeric micelles with in-situ gelation for enhanced ocular delivery of Ketoconazole. Journal of Pharmaceutical Innovation. 2025;20(1):1-2. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12247-024-09915-w.
CrossRef - Kotta S, Khan AW, Ansari SH, Sharma RK, Ali J. Formulation of nanoemulsion: a comparison between phase inversion composition method and high-pressure homogenization method. Drug delivery. 2015;22(4):455-66. DOI: 10.3109/10717544.2013.866992
CrossRef - Shevalkar G, Vavia P. Solidified nanostructured lipid carrier (S-NLC) for enhancing the oral bioavailability of ezetimibe. Journal of drug delivery science and technology. 2019;53:101211. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101211.
CrossRef - Salunkhe SS, Bhatia NM, Thorat JD, Choudhari PB, Bhatia MS. Formulation, development and evaluation of ibuprofen loaded nanoemulsion prepared by nanoprecipitation technique: use of factorial design approach as a tool of optimization methodology. Journal of pharmaceutical investigation. 2014;44:273-90. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-014-0125-4.
CrossRef - Nasser ST, Abdulrassol A, Ghareeb M M.Design, Preparation and In-vitro Evaluation of Novel Ocular Antifungal Nanoemulsion Using Posaconazole as a Model Drug. International Journal of Drug Delivery Technology. 2021;11(3):1-7. DOI: 10.25258/ijddt.11.3.71.
- Paliwal S, Kaur G, Arya RK. Formulation and characterization of topical nano emulgel of terbinafine. Universal Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 2018;3(6):doi:10.22270/ujpr.v3i6.223.
CrossRef - Ahmad I, Farheen M, Kukreti A, et al. Natural oils enhance the topical delivery of ketoconazole by nanoemulgel for fungal infections. ACS omega. 2023;8(31):28233-48. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.3c01571.
CrossRef - Bhattacharya SA, Prajapati BG. Formulation and optimization of celecoxib nanoemulgel. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research.2017;10(8):353-65.https://doi.org/10.22159/ ajpcr.2017.v10i8.19510
CrossRef - Shevalkar G, Pai R, Vavia P. Nanostructured lipid carrier of propofol: a promising alternative to marketed soybean oil–based nanoemulsion. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019 ; 28;20(5):201. DOI :; 10.1208/s12249-019-1408-x.
CrossRef - Mahtab A, Anwar M, Mallick N, Naz Z, Jain GK, Ahmad FJ. Transungual delivery of ketoconazole nanoemulgel for the effective management of onychomycosis. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016;17(6):1477-1490. DOI : 10.1208/s12249-016-0488-0.
CrossRef - Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. Journal of pharmaceutical analysis. 2016;6(2):71-79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2015.11.005.
CrossRef - Tayah DY, Eid AM. Development of miconazole nitrate nanoparticles loaded in nanoemulgel to improve its antifungal activity. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 2023;31(4):526-34. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.005.
CrossRef - Dhawan B, Aggarwal G, Harikumar SL. Enhanced transdermal permeability of piroxicam through novel nanoemulgel formulation. International journal of pharmaceutical investigation. 20144(2):65-76. Doi: 10.4103/2230-973X.133053.
CrossRef - Na Nan, S., Luckanagul, J. A., & Panapisal, V. R. The Impact of Surfactant Structures and High-Speed Mixing Dynamics in Achieving Nano-Sized Emulsions with Simple High-Speed Homogenization. Nanotechnology, Science and Applications,2024, 17, 273–288.DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/ NSA.S492639.
CrossRef - Kumar M, Bishnoi RS, Shukla AK, Jain CP. Techniques for Formulation of Nanoemulsion Drug Delivery System: A Review. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2019 Sep;24(3):225-234. doi: 10.3746/pnf. 2019.24.3.225. Epub 2019 Sep 30. PMID: 31608247; PMCID: PMC6779084.
CrossRef - Gawin-Mikołajewicz A, Nawrot U, Malec KH, Krajewska K, Nartowski KP, Karolewicz BL. The Effect of High-Pressure Homogenization Conditions on the Physicochemical Properties and Stability of Designed Fluconazole-Loaded Ocular Nanoemulsions. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16010011.
CrossRef
Abbreviations List
UV: Ultra Violet
DSC: Differential scanning colorimetry
PEG: Polyethylene glycol
Cp: Centipoise

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





