Manuscript accepted on : 06-09-2025
Published online on: 17-09-2025
Plagiarism Check: Yes
Reviewed by: Dr. Md. Sarwar Hossain
Second Review by: Dr. Mohamed Nader
Final Approval by: Dr. Wagih Ghannam
Kiran Prakash Surywanshi1 , Shivraj Popat Jadhav1*
, Shivraj Popat Jadhav1* , Khemchand Rajendra Surana2
, Khemchand Rajendra Surana2 , Parag Ashok Pathade3
, Parag Ashok Pathade3 and Sunil Kashinath Mahajan2
and Sunil Kashinath Mahajan2
1Department of Pharmaceutics, Divine College of Pharmacy, Satana, Nashik, Maharashtra, India
2Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Divine College of Pharmacy, Satana, Nashik, Maharashtra, India
3Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, KBHSS Trust’s Institute of Pharmacy, Malegaon, Nashik, Maharashtra, India
Corresponding Author E-mail:shiva.007ind@gmail.com
ABSTRACT: Remogliflozin etabonate, a selective inhibitor of SGLT2, is prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus. To support quality control and routine testing, a dependable and efficient analytical technique is essential. The present study consists of a rapid, precise, and straightforward Reverse-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC) method development for quantifying remogliflozin etabonate. An Inertsil ODS-3V column (150*4.6 mm, 5 µm) was used for separation. Optimization of the mobile phase was done from methanol: water (70:30, v/v) to acetonitrile: water (75:25, v/v), flow rate of 1.0 mL/min, and samples were analysed at 230 nm using a UV detector. ICH Q2(R1) was followed for validation of the method to assess various parameters like linearity, accuracy, precision, robustness, LOD, and LOQ. The assay demonstrated excellent linearity over 10–50 µg/mL (R² = 0.999), with a retention time of 2.55 min. Precision results showed %RSD values below 2%, while recovery studies confirmed accuracy within 98–102%. The calculated LOD and LOQ were 0.22 µg/mL and 0.68 µg/mL, respectively. The validated technique proved to be simple and robust, with adequate specificity, and can be effectively applied for routine analysis of remogliflozin etabonate in bulk as well as pharmaceuticals.
KEYWORDS: Method development; Remogliflozin etabonate; RP-HPLC; SGLT2 inhibitor; Validation
| Copy the following to cite this article: Surywanshi K. P, Jadhav S. P, Surana K. R. Pathade P. A, Mahajan S. K. Development and Validation of a Robust RP-HPLC Method for the Estimation of Remogliflozin Etabonate in Bulk and Tablet Dosage Forms. Biotech Res Asia 2025;22(3). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Surywanshi K. P, Jadhav S. P, Surana K. R. Pathade P. A, Mahajan S. K. Development and Validation of a Robust RP-HPLC Method for the Estimation of Remogliflozin Etabonate in Bulk and Tablet Dosage Forms. Biotech Res Asia 2025;22(3). Available from: https://bit.ly/4gpDvAh |
Introduction
Remogliflozin etabonate is an orally-active prodrug with the therapeutic effect of the sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, a novel type of antidiabetic agent that acts regardless of insulin.1,2 Once administered, it is rapidly hydrolyzed to its active metabolite, remogliflozin, which selectively inhibits SGLT2 proteins located in the proximal renal tubules. This inhibition reduces glucose reabsorption and surges urinary glucose excretion (glycosuria), thereby keeping in check hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Due to its unique mechanism, remogliflozin etabonate is not only effective in glycemic control but also contributes to modest weight loss and blood pressure reduction, making it a promising option for the comprehensive management of T2DM.3,4
As the therapeutic use of remogliflozin etabonate continues to expand, there arises a significant necessity for a specific and reliable analytical method to confirm its quality, effectiveness, and safety during formulation development and routine pharmaceutical analysis. While various techniques, including UV-spectrophotometry and LC-MS, have been employed for the analysis of remogliflozin or its metabolites, these methods often require complex sample preparation, higher cost, or lack the simplicity needed for quality control environments in developing laboratories.5
One of the most used analysis methods in the pharmaceutical field is RP-HPLC, since it is highly robust, sensitive, and versatile in a variety of uses and applications. However, the literature still lacks comprehensive, validated RP-HPLC methods tailored specifically for remogliflozin etabonate in both bulk and formulated dosage forms.6-8
Thus, the present paper proposes the development and validation of a novel and less complicated, precise, and fast RP-HPLC method that could be used to quantitatively estimate remogliflozin etabonate. This procedure is validated according to the ICH Q2(R1), with crucial parameters that include linearity, accuracy, precision, robustness, with the limit of detection (LOD) as well as quantification (LOQ). The final objective is to have a validated analytical device, which could be standardized to be used regularly in the lab of quality control.
Materials and Methods
Material
Remogliflozin etabonate standard was received as a gifted sample from Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Methanol and acetonitrile (Sigma Aldrich, HPLC grade) were purchased through Sudarshan Scientific Limited, Nandgaon. In the case of this study, water (double distilled) was utilized.
Instrumentation
Chromatographic analysis was done on a SHIMADZU LC-20AT HPLC unit consisting of a binary gradient pump, a manual Rheodyne injector with a 20 μL sample loop, and a UV-visible detector (SPD-20A). The acquisition and data processing were made with the LabSolutions software. Ambient temperature conditions were used to separate the sample using an Inertsil ODS-3V column.
The mobile consisted of methanol: water in a 70:30 ratio. The mobile phase was passed through a filter membrane of 0.45 µm and sonicated for 10 minutes before use. Before analysis, the chromatographic system was conditioned with the mobile phase for a minimum of 30 minutes.
Selection of analytical wavelength
A 20 ppm solution of Remogliflozin etabonate with methanol as a blank was scanned between 200 to 400 nm in a UV visible spectrophotometer (Jasco UV550) to determine the absorption maxima of Remogliflozin etabonate.9
Preparation of mobile phase
Initially, a Methanol: Water system was tested; however, method development and validation were performed by using Acetonitrile: Water (75:25 v/v), which was mixed, ultrasonically degassed for 10–15 minutes, by use of 0.45 µm filter, filtration was carried out.10
Preparation of Standard Stock Solution
25 mg of the remogliflozin etabonate was weighed accurately, followed by solubilisation in 50 mL of methanol, to yield a stock solution of 500 ppm. Further dilution was done to get a solution of 25 ppm.11
Preparation of sample for assay
Twenty Remo-Zen (100 mg) tablets were weighed, powdered, and a portion equivalent to 25 mg of remogliflozin etabonate was taken in a volumetric flask of 50 mL. Initially, 35 ml of methanol is added to the flask and then sonicated for 15 minutes, and then the final volume is adjusted. Filtration of the solution was then carried out by use of a 0.45 µm nylon syringe filter. 1 mL of the filtrate was further diluted to 20 mL with mobile phase to obtain a 25 µg/mL working solution for RP-HPLC.12
Method Development
Modification of the mobile phase conditions allowed refinement of the method, producing sharper peaks with better symmetry, lower tailing, and consistent retention behaviour.
Trial 1
The initial trial employed Methanol: Water (70:30 v/v) as a mobile phase. Although the remogliflozin etabonate was eluted, the chromatogram displayed a broad and asymmetric peak, with high retention time and poor resolution. Therefore, the next trial was conducted.
Trial 2
The same Methanol: Water (60:40 v/v) ratio was used, and the detection wavelength was optimized to 228 nm using UV-visible spectrophotometric analysis. A slight improvement in peak shape was observed, but the tailing factor remained high, and the theoretical plate count was below the suitable limit.
Trial 3
In this trial, methanol was substituted with acetonitrile to improve peak symmetry and shorten the retention time. The mobile phase was then adjusted to acetonitrile: water (70:30, v/v). This modification resulted in a significant enhancement in both peak shape and retention time, demonstrating that acetonitrile serves as a more effective organic modifier for remogliflozin etabonate.
Trial 4
Using an acetonitrile–water mobile phase (75:25, v/v) afforded a sharp, symmetrical peak at about 3.2 min with a 1.0 mL per minute flow rate at 228 nm, 40 °C column oven temperature, and a 20 µL injection volume.
Method Validation
The quantitative estimation of remogliflozin etabonate was optimized using an RP-HPLC method in accordance with ICH Q2(R1). Validation assessed linearity, accuracy, precision, specificity, robustness, solution stability, and the limits of detection and quantitation (LOD, LOQ).
Linearity and Range
Across 2.5–37.5 µg/mL—corresponding to 10–150% of the target concentration—linearity was assessed using multiple standards, each injected in triplicate. The peak area–concentration plot yielded a correlation coefficient (r²) exceeding 0.999.13
Accuracy (% Recovery)
To evaluate accuracy, known quantities of the standard were spiked into the placebo at 50, 100, and 150 % of the target concentration, measuring each concentration in tripilicate.14
Precision
The method’s precision was confirmed via intra-day repeatability and inter-day intermediate precision studies, each based on six replicate analyses of a 25 µg/mL solution; %RSD was calculated for both sets.15
Specificity
Specificity was assessed by analysing blank samples (containing only the solvent), placebo samples (comprising all excipients without the active drug), and test samples (containing the analyte along with excipients) to confirm that the method accurately distinguishes the analyte response from potential interferences.16
Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantitation (LOQ):17
These values were computed by using the following equations;

Robustness
Robustness was evaluated by deliberately varying the rate of flow by ±0.1, the wavelength of detection by ±2, and the temperature of the column by ±2 °C. These modifications did not produce any significant impact on chromatographic performance, confirming the method’s robustness.¹⁸
Solution Stability
Both standard and sample solutions were assessed for stability at room temperature over 24 hours. No significant variations in peak area or retention time were observed, with percentage differences remaining within ±2%, indicating good solution stability.19
Result
Selection of analytical wavelength
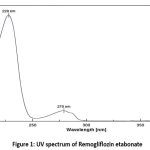 |
Figure 1: UV spectrum of Remogliflozin etabonateClick here to View Figure |
Remogliflozin etabonate exhibited its highest absorbance at 228 nm, as illustrated in Figure 1; hence, this wavelength was selected as the analytical wavelength for subsequent analysis.
Method optimization
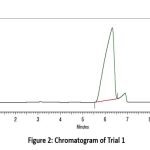 |
Figure 2: Chromatogram of Trial 1Click here to View Figure |
In Trial 1, the chromatogram obtained using Methanol: Water (70:30 v/v) displayed a broad and asymmetric peak with significant tailing at approximately 6 minutes. The inadequate peak shape, poor resolution, and high retention time indicated that the chromatographic conditions were suboptimal for Remogliflozin etabonate. Consequently, this trial was deemed unsuitable, and further optimization of the mobile phase and detection parameters was pursued in subsequent trials.
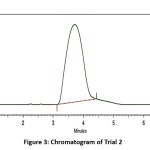 |
Figure 3: Chromatogram of Trial 2Click here to View Figure |
The use of methanol and water in a 70:30 (v/v) ratio as the mobile phase led to a shorter retention time of approximately four minutes, while also enhancing peak sharpness in comparison with the earlier trial. However, significant peak tailing persisted, and the system’s theoretical plate count remained below acceptable limits. The peak did not return rapidly to the baseline, which could compromise quantification accuracy and reproducibility. Consequently, this set of conditions was also deemed suboptimal, necessitating further optimization in subsequent trials.
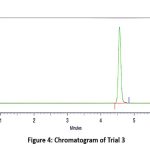 |
Figure 4: Chromatogram of Trial 3.Click here to View Figure |
In this trial, the mobile phase was switched from methanol to acetonitrile (Acetonitrile: Water 70:30 v/v). This modification led to a sharp, symmetrical peak for Remogliflozin etabonate at a retention time of approximately 4.7 minutes. The chromatogram displayed minimal tailing, high sensitivity, and a stable baseline, with a theoretical plate count well above acceptable limits. The significant improvements in peak shape, efficiency, and analysis time demonstrated that acetonitrile is a more suitable organic solvent for the RP-HPLC estimation of Remogliflozin etabonate compared to methanol. However, further fine-tuning of the mobile phase ratio was undertaken in the subsequent trial to achieve optimal performance.
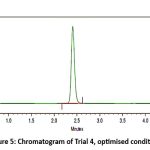 |
Figure 5: Chromatogram of Trial 4, optimised conditions.Click here to View Figure |
Further alteration of the mobile phase to Acetonitrile: Water (75:25 v/v) yielded a highly symmetrical and sharp peak for Remogliflozin etabonate, having 2.5 minutes as a retention time.. This trial demonstrated superior chromatographic performance, including rapid elution, a stable baseline, and a high signal-to-noise ratio. No interference was observed, confirming the specificity of the method. Table 1 outlines the optimised conditions.
Table 1: Optimized Chromatographic Conditions for RP-HPLC Analysis of Remogliflozin Etabonate
| Parameter | Description |
| Chromatographic Mode | Isocratic Elution |
| Stationary Phase | Inertsil ODS-3V, |
| Detection System | Ultraviolet Detector |
| Volume of Injection | 20 μL |
| Detection Wavelength | 228 nm |
| Temperature of the Column | 40°C |
| Composition of Mobile Phase | Acetonitrile: Water (75:25, v/v) |
| Rate of Flow | 1.0 mL per minute |
| Total Run Time | 5 minutes |
Method Validation
As per ICH and FDA standards, the method was validated on the following parameters.
Linearity and Range
As presented in Figure 6, the calibration curve of peak area versus concentration showed outstanding linearity, with an r² value of 0.9999, validating the proportional relationship between analyte concentration and detector response.
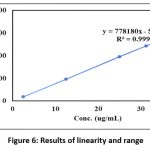 |
Figure 6: Results of linearity and rangeClick here to View Figure |
Accuracy
Recovery-based accuracy was assessed at 50%, 100%, and 150% of the target concentration by spiking a placebo with known amounts of remogliflozin etabonate; each level was analyzed in triplicate (Table 2). Mean recoveries were 98.76% (0.4088% RSD), 99.88% (1.0032% RSD), and 99.62% (0.6362% RSD) at the 50%, 100%, and 150% levels, respectively. All recoveries met the 98–102% criterion with %RSD <2%, demonstrating accuracy, reliability, and negligible matrix effects, suitable for precise assay of the drug in formulations.
Table 2: Accuracy (% Recovery) of Remogliflozin Etabonate by RP-HPLC
| Spiking Level | Peak Area | Measured Concentration (µg/mL) | Nominal Concentration (µg/mL) | % of Drug Recovered | Average Recovery (%) | % RSD |
| 50% | 9,793,560 | 12.53 | 12.70 | 98.66 | 98.76 | 0.4088 |
| 9,695,821 | 12.40 | 12.50 | 99.20 | |||
| 9,693,682 | 12.40 | 12.60 | 98.41 | |||
| 100% | 68,593 | 25.03 | 25.20 | 99.33 | 99.88 | 1.0032 |
| 19,406,808 | 24.82 | 25.00 | 99.28 | |||
| 19,825,604 | 25.36 | 25.10 | 101.04 | |||
| 150% | 29,568,630 | 37.82 | 37.70 | 100.32 | 99.62 | 0.6362 |
| 29,054,856 | 37.16 | 37.50 | 99.09 | |||
| 29,156,921 | 37.29 | 37.50 | 99.44 |
Precision
The precision of the developed method for estimating remogliflozin etabonate was assessed through repeatability and intermediate precision studies. For repeatability, 6 replicate injections of the same sample were analyzed under the same conditions on the same day, yielding % assay values between 97.42% and 101.06%, with a mean of 99.18%, a SD of 1.2609, and a %RSD of 1.271, demonstrating excellent repeatability. The precision results are presented in Table 3.
Intermediate precision was assessed on a different day by a different analyst using the same equipment. The % assay values ranged from 96.82 % to 100.18 %, with an average of 98.46 %, SD of 1.2789, and % RSD of 1.299, confirming inter-day reproducibility.
The overall precision, combining both intra-day and inter-day data, yielded an average assay of 98.82 %, SD of 1.2684, and % RSD of 1.284, which are within the acceptable limit of < 2% RSD as per ICH guidelines. These results confirm that the method is precise and reliable for routine analytical use.
Table 3: Results of precision
| Parameter | Sample | Weight (mg) | Area | % Assay |
| Repeatability | 1 | 116.9 | 19,235,204 | 98.38 |
| 2 | 117.1 | 19,352,605 | 98.81 | |
| 3 | 116.5 | 19,428,689 | 99.71 | |
| 4 | 116.8 | 19,030,458 | 97.42 | |
| 5 | 117.3 | 19,558,204 | 99.69 | |
| 6 | 116.7 | 19,725,036 | 101.06 | |
| Mean | 99.18 | |||
| Standard Deviation | 1.2609 | |||
| % RSD | 1.271 | |||
| Intermediate Precision | 1 | 117.2 | 19,063,024 | 97.25 |
| 2 | 116.6 | 19,402,530 | 99.49 | |
| 3 | 116.9 | 19,250,350 | 98.46 | |
| 4 | 117.1 | 19,620,454 | 100.18 | |
| 5 | 116.8 | 19,248,726 | 98.53 | |
| 6 | 116.5 | 18,865,274 | 96.82 | |
| Mean | 98.46 | |||
| Standard Deviation | 1.2789 | |||
| % RSD | 1.299 | |||
| Overall Precision (Average) | – | – | – | 98.82 |
| Overall Standard Deviation | – | – | – | 1.2684 |
| Overall % RSD | – | – | – | 1.284 |
Specificity
Blank, placebo, standard, and test solutions were analysed to confirm the specificity. There was no interference at the retention time of Remogliflozin Etabonate from either the blank or the placebo, indicating that the method selectively quantifies the analyte without interference from excipients or solvent components. Table 4 outlines the results of specificity.
Peak purity, determined by diode-array detection, was 0.989 for the standard and 0.985 for the test solution, i.e., near 1.000. This confirms that the peaks were spectrally pure and not co-eluting with any other component, thereby establishing the specificity of the developed method.
Table 4: Result of Specificity
| Sample Type | Observation/Result |
| Blank | No peak observed at the retention time (RT) of Remogliflozin Etabonate |
| Placebo | No interfering peak detected at the RT of Remogliflozin Etabonate |
| Standard Preparation | Peak purity index recorded at 0.989 |
| Test Preparation | Peak purity index recorded at 0.985 |
LOD and LOQ
Sensitivity was evaluated per ICH Q2(R1) by determining LOD and LOQ from the response SD (σ = 52944.1) and calibration slope (S = 778180). The LOD was 0.2245 µg/mL and the LOQ was 0.6801 µg/mL. Table 5 indicates that these values confirm high sensitivity for detecting and quantifying remogliflozin etabonate.
Table 5: Results of LOD and LOQ
| Parameter | Value | Formula Used | Inputs |
| LOD | 0.22 µg/mL | LOD=(3.3×σ)/S | σ=52944.1,S=778180 |
| LOQ | 0.68 µg/mL | LOQ=(10×σ)/S |
Robustness
The RP-HPLC method was tested for robustness through deliberate alterations in analytical conditions, including flow rate (±10%), detection wavelength (±3 nm), and column oven temperature (±2°C). Chromatographic performance was assessed on the grounds of retention time, peak area, asymmetry, and theoretical plate count, with results summarized in Table 6. These variations did not produce any significant impact on retention time or system suitability parameters. Retention times ranged from 2.18 to 2.69 minutes, asymmetry factors remained within the acceptable range (1.16–1.22), and theoretical plates varied between 6415 and 6936, indicating consistent column efficiency. These findings confirm that the developed method is robust and dependable under varied analytical conditions.
Table 6: Results of Robustness
| Modified Analytical Condition | Retention Time (min) | Peak Area (AU) | Peak Asymmetry Factor | Column Efficiency |
| Wavelength +3 nm(231 nm) | 2.40 | 13,467,094 | 1.19 | 6629 |
| Wavelength –3 nm(225 nm) | 2.41 | 28,801,603 | 1.20 | 6684 |
| Flow rate +10%(1.1 mL/min) | 2.18 | 17,360,892 | 1.16 | 6415 |
| Flow rate –10%(0.9 mL/min) | 2.69 | 22,486,934 | 1.22 | 6936 |
| Column oven temp + 2°C (42°C) | 2.41 | 19,560,395 | 1.19 | 6672 |
| Column oven temp – 2°C (38°C) | 2.42 | 19,238,642 | 1.18 | 6517 |
Saturation Solubility
The solution stability of Remogliflozin Etabonate was assessed by monitoring the peak area of standard and sample solutions at room temperature over 24 hours. The % absolute difference in area values was found to be less than ±2% for both standard and sample solutions at 12 and 24 hours when compared to initial values. Results, as shown in Table 7, indicated that the solutions remained stable with no significant degradation or variation in chromatographic response. Therefore, the method is reliable for routine analysis when solutions are used within 24 hours under room temperature conditions.
Table 7: Results of solution stability
| Type | Time Interval | Peak Area (AU) | % Change from Initial |
| Sample Solution | Initial | 19,493,256 | NA |
| 12 Hours | 19,350,369 | 0.73% | |
| 24 Hours | 19,316,356 | 0.91% | |
| Standard Solution | Initial | 19,625,038 | NA |
| 12 Hours | 19,505,069 | 0.61% | |
| 24 Hours | 19,460,148 | 0.84% |
Assay of Marketed Tablets
Quantitative estimation of Remogliflozin etabonate in a marketed tablet (Remo-Zen 100 mg) was performed successfully by a validated RP-HPLC method. Following the described method, the prepared sample was introduced into the system under optimized chromatographic conditions. The amount of Remogliflozin Etabonate available in the tablet dosage form was estimated by using the peak area of the sample by comparing with the standard. The analysis showed that the formulation contained 98.76% of the labelled amount of drug.
Discussion
The primary objective of this study was to develop and validate a reliable, accurate, and robust RP-HPLC technique for the quantification of Remogliflozin Etabonate in bulk and pharmaceuticals. The method was optimized to ensure high sensitivity, reproducibility, and specificity, essential for day-to-day quality control in pharmaceuticals.
During system development, various mobile phase compositions and chromatographic parameters were evaluated. The transition from methanol to acetonitrile as the organic solvent significantly enhanced peak shape and reduced retention time. The final optimized mobile phase—Acetonitrile: Water (75:25, v/v)—provided a sharp, symmetrical peak at a retention time of approximately 2.5 minutes, indicating rapid and efficient elution. This composition also improved resolution and minimized peak tailing, addressing limitations seen in earlier trials.
The method demonstrated excellent linearity (r² = 0.9999) across a wide concentration range (2.5–37.5 µg/mL), confirming its suitability for quantifying varying drug concentrations. The accuracy, as reflected in recovery studies ranging from 98.41% to 101.04%, confirmed that the method accurately measures the analyte without interference from excipients. Additionally, the % RSD values for accuracy and precision were consistently below 2%, which is well within ICH Q2(R1) guidelines, further affirming the reliability and repeatability of the method.
Sensitivity parameters – LOD (0.22 µg/mL) and LOQ (0.68 µg/mL) – highlight the method’s ability to detect and quantify even trace amounts of Remogliflozin Etabonate. These values are notably lower than those reported in several previous analytical methods, suggesting improved sensitivity compared to existing literature.
The absence of interfering peaks in blank and placebo chromatograms confirmed method specificity, while peak purity index values (>0.98) indicated no co-elution. This makes the method highly specific for Remogliflozin Etabonate, ensuring reliable results even in complex matrices.
Robustness testing validated that a slight intentional change in chromatographic situations, such as flow rate, temperature, and detection wavelength, did not significantly impact method performance. Moreover, solution stability was maintained over 24 hours, ensuring practicality for routine laboratory use without immediate degradation concerns.
The assay of the marketed tablet formulation (Remo-Zen 100 mg) demonstrated a drug content of 98.76%, which is within acceptable pharmacopeial limits. This further confirms the applicability of the method for real-world pharmaceutical analysis, reinforcing its effectiveness for batch consistency and regulatory compliance.
Overall, the developed RP-HPLC method addresses key analytical challenges by offering simplicity, speed, accuracy, and reproducibility, which are important for ensuring the therapeutic efficacy and safety of Remogliflozin Etabonate. While the current technique is well-suited for day-to-day quality control of Remogliflozin Etabonate in tablet dosage forms, future studies can expand its application to plasma or urine analysis for pharmacokinetic and bioequivalence studies. Further development of stability-indicating methods under various stress conditions (e.g., oxidative, photolytic, thermal) could strengthen their utility in stability testing.
Conclusion
A rapid, simple, and robust RP-HPLC method was developed and validated for quantifying remogliflozin etabonate in bulk and tablet forms. Using acetonitrile–water (75:25, v/v) as the mobile phase, the optimized conditions produced sharp, symmetrical peaks with a ~2.5-min retention time. The method showed excellent linearity (r² = 0.9999), high precision (%RSD < 2%), and accuracy (98–102% recovery). Low LOD (0.22 µg/mL) and LOQ (0.68 µg/mL) demonstrated sensitivity for trace levels. It was also specific, robust to minor changes, and stable over 24 h. Assay of marketed products confirmed applicability. Overall, the method is suitable for routine QC and potentially useful for bioanalytical and stability studies.
Acknowledgement
Authors are thankful to the Divine College of Pharmacy, Satana for providing necessary infrastructure to carry out this research work.
Funding Sources
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of Interest
The authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Data Availability Statement
This statement does not apply to this article.
Ethics Statement
This research did not involve human participants, animal subjects, or any material that requires ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
This study did not involve human participants, and therefore, informed consent was not required.
Clinical Trial Registration
This research does not involve any clinical trials.
Permission to reproduce material from other sources
Not Applicable
Author Contributions
Kiran Prakash Surywanshi: Conducted the experimental work, data acquisition, and initial drafting of the manuscript
Shivraj Popat Jadhav: Conceptualized and supervised the study, optimized the experimental design, and critically revised the manuscript;
Khemchand Rajendra Surana: Assisted in analytical method validation, data analysis, and interpretation of results;
Parag Ashok Pathade: Contributed to the literature review, data interpretation, and manuscript editing for technical accuracy;
Sunil Kashinath Mahajan: Supported in instrumentation setup, troubleshooting, and final proof-reading.
References
- Fujimori Y, Katsuno K, Nakashima I, Ishikawa-Takemura Y, Fujikura H, Isaji M. Remogliflozin etabonate, in a novel category of selective low-affinity sodium glucose cotransporter (SGLT2) inhibitors, exhibits antidiabetic efficacy in rodent models. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;327(2):268-276. DOI: 1124/jpet.108.140210
CrossRef - Mohan V, Mithal A, Joshi SR, Aravind SR, Chowdhury S. Remogliflozin etabonate in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: design, development, and place in therapy. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:2487-2501. DOI: 2147/DDDT.S221093.
CrossRef - Hussey EK, Kapur A, O’Connor-Semmes R, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of remogliflozin etabonate, a novel SGLT2 inhibitor, and metformin when co-administered in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013;14:25. DOI: 1186/2050-6511-14-25
CrossRef - Mikhail N. Remogliflozin etabonate: a novel SGLT2 inhibitor for treatment of diabetes mellitus. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015;24(11):1381-1387. DOI: 1517/13543784.2015.1061501
CrossRef - Kumar SD, Kumar DH. Importance of RP-HPLC in analytical method development: a review. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2012;3(12):4626-4633. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.3(12).4626-33
CrossRef - Kumar D, Kumar A, Kumar V, Raj A, Baliyan V, Kumar NA. A comprehensive review on analytical method development using RP-HPLC and recent advances in pharmaceutical applications. J Res Appl Sci Biotechnol. 2023;2(2):53-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.55544/jrasb.2.2.9
CrossRef - Jumde HS, Mankar SD. Review on development of analytical method and validation by reverse phase–high performance liquid chromatography. Asian J Pharm Technol. 2022;12(3):179-182. DOI: 52711/2231-5713.2022.00030
CrossRef - Pund S, Nalawade S, Rajurkar V, Jayatpal S, Deshmukh N, Tare H. A brief review on recent advances in reverse phase HPLC. Multidiscip Rev. 2024;7:2024072. DOI: https://10.31893/multirev.2024072
CrossRef - Jadhav KR, Sonawane VN, Jadhav SP, Somvanshi DB, Patil CD. Method development and validation for estimation of melatonin in tablet by using RP-HPLC. J Med Pharm Allied Sci. 2021;IC1-I1:54-61. DOI: 22270/jmpas.2021.IC1I1.1922
CrossRef - Adilakshmi N. A novel RP-HPLC methodology for method development and validation of aceclofenac and tizanidine pharmaceutical dosage forms. J Adv Pharm Res. 2020;8(1):33-44. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.joapr.2020.v.8.i.4.33.44
CrossRef - Itigimatha N, Chadchan KS, Yallur BC, Hadagali MD. Simple and sensitive RP-HPLC and UV spectroscopic methods for the determination of remogliflozin etabonate in pure and pharmaceutical formulations. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2022;19(2):213-219. DOI: 4274/tjps.galenos.2021.55381
CrossRef - Patel VS, Kapupara PP. Stability indicating RP-HPLC method development and validation for the simultaneous quantification of remogliflozin etabonate and metformin HCl. Indian J Pharm Educ Res. 2025;59(suppl 1):S274-S282. DOI: 5530/ijper.20253781
CrossRef - Ismail R, Lee HY, Mahyudin NA, Abu Bakar F. Linearity study on detection and quantification limits for the determination of avermectins using linear regression. J Food Drug Anal. 2014;22(3):407-412. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2014.01.026
CrossRef - Betz JM, Brown PN, Roman MC. Accuracy, precision, and reliability of chemical measurements in natural products research. Fitoterapia. 2011;82(1):44-52. DOI: 1016/j.fitote.2010.09.011
CrossRef - Dhondage A, Jadhav S, Patil D, Pathade P, Deore R, Ahire Y. Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for determination of rifapentine and moxifloxacin hydrochloride in bulk and tablet dosage form. J Pharm Negat Results. 2022;13(special issue 7):4510-4518. DOI: https://doi.org/10.47750/pnr.2022.13.S07.564
- Le H, Phung TH, Le DC. Development and validation of an HPLC method for simultaneous assay of potassium guaiacolsulfonate and sodium benzoate in pediatric oral powder. J Anal Methods Chem. 2019;2019:6143061. DOI: 1155/2019/6143061
CrossRef - Little T. Method validation essentials: limit of blank, limit of detection, and limit of quantitation. BioPharm Int. 2015;28(4).
- Patel KY, Dedania ZR, Dedania RR, et al. QbD approach to HPLC method development and validation of ceftriaxone sodium. Future J Pharm Sci. 2021;7:141. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-021-00286-4
CrossRef - Fathima H, Havannavar NT, Jahan A. Estimation and validation of remogliflozin etabonate in dosage form and in bulk drug by spectrophotometric method. Asian J Res Chem. 2022;15(3):166-170. DOI: 52711/0974-4150.2022.00028
CrossRef

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





